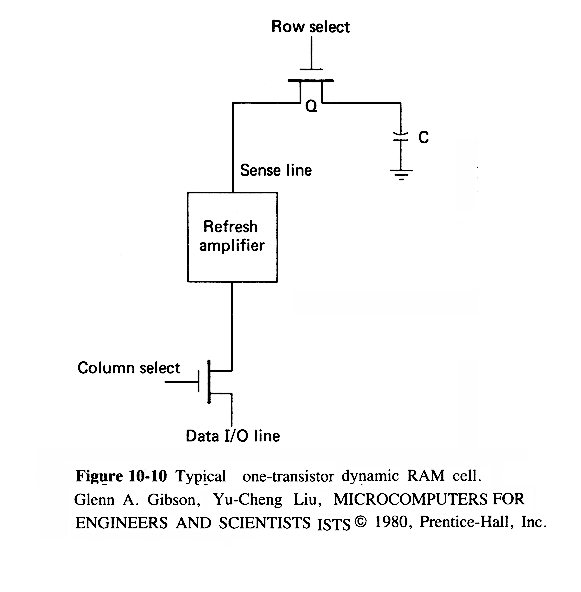
In a memory refresh cycle, a row address is sent to the memory
chips and a read operation is performed to refresh the selected row of
cells.However, a refresh cycle differs fro a regular memory read cycle
in the following respects:
- The address input to the memory chips does not come from the address
bus.Instead, the row address is supplied by a binary counter called the
refresh address counter.This counter is incremented by one for
each memory refresh cycle so that it sequences through all the row addresses.
The column address is not involved because all elements in a row are
refreshed simultaneously.
- During a memory refresh cycle, all memory chips are enabled so that
memory refresh is performed on every chip in the memory module simultaneously.
This reduces the number of refresh cycles.In a regular read cycle, at
most one row of memory chips is enabled.
- In addition to the chip enable control input, normally a dynamic RAM
has a data output enable control.These two control inputs are combined
internally so that the data output is forced to its high-impedance mode
unless both control inputs are activated.During a memory refresh cycle, the
data output enable control is deactivated.

