A block transfer is a succession of the datum transfers described above. Each successive DMA uses the next consecutive memory location.
The activity involved in transferring a byte or word over the system bus is called a bus cycle. The execution of an instruction may require more than one bus cycle. For example the instruction:
MOV AL, TOTALwould use a bus cycle to bring in the contents of TOTAL in addition to the cycle needed to fetch the instruction.
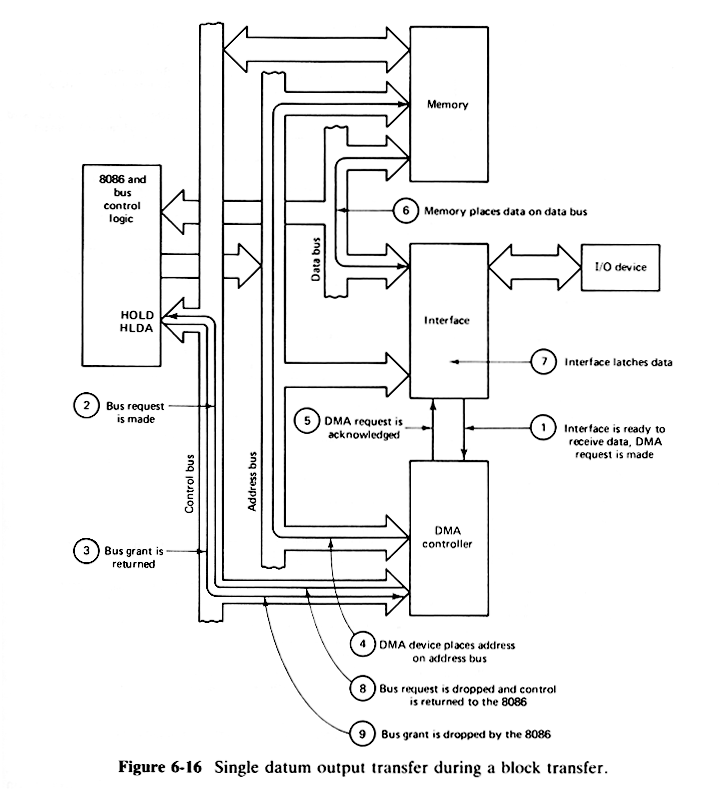
The 8086 receives bus requests through its HOLD pin and issues grants from
its hold acknowledge (HLDA) pin. A request is made when a potential master
sends a 1 to the HOLD pin. Normally, after the current bus cycle is complete
the 8086 will respond by putting a 1 on the HLDA pin. When the requesting device
receives this grant signal it becomes the master. It will remain master until it
drops the signal to the HOLD pin, at which time the 8086 will drop the grant on
the HLDA pin.

A block transfer is a succession of the datum transfers described above.
Each successive DMA uses the next consecutive memory location.
| PRETHODNA FOLIJA | SADRZAJ | SLEDECA FOLIJA |