A typical sequence for starting a block input transfer is given
in Fig.6-18. This sequence assumes the following bit definitions:
Bit 2 of INTSTAT-Busy bit for the I/O device
Bit 1 of DMACON-Informs the controller of the transfer direction; 1
is for input
Bit 3 of DMACON-Enables the controller so it will accept DMA requests
Bit 6 of DMACON-Clear when bus is to be relinquished between transfers
Bit 0 of INTCON-Informs the interface of the transfer direction; 1
is for input
Bit 2 of INTCON-Do bit which starts the I/O activity
After the sequence in Fig.6-18 is executed the I/O device will begin inputting
data and the DMA controller will steal a bus cycle and transfer a byte from the
interface to memory each time a byte is placed in the interface's data-in buffer
register.
Figure 6-18 Typical sequence for initiating a block transfer
IDLE: IN AL, INTSTAT ;LOOP UNTIL DEVICE IS FREE
TEST AL, 4
JNZ IDLE
MOV AX, BYTE_COUNT ;PUT BLOCK SIZE IN
OUT BC_REG, AX ;BYTE COUNT REGISTER
LEA AX, BUFFER ;PUT BEGINNING ADDRESS
OUT ADDR_REG, AX ;IN ADDRESS REGISTER
MOV AL, DMAC ;SET DIRECTION AND ENABLE
OR AL, 0AH ;BITS IN CONTROL BYTE AND
OUT DMACON, AL ;OUTPUT TO CONTROLLER
MOV AL, INTC ;SET DIRECTION AND DO BIT
OR AL, 5 ;IN THE INTERFACE COMMAND
OUT INTCON, AL ;REGISTER
.
.
.
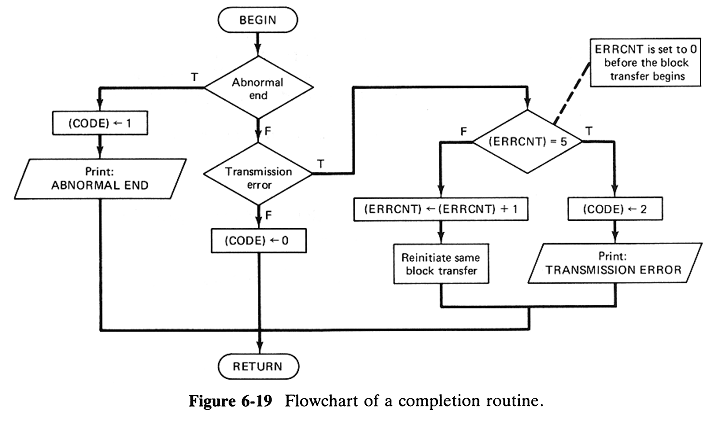
Figure 6-19 is a flowchart of a completion routine that is designed
to follow a disk input transfer. The routine checks for abnormal end
and transmission errors.
If an interface is connected to a nonstorage device then the minimal
configuration shown in Fig.6-17 may be adequate but for a storage device
the interface needs to communicate search and address information to the device.
The interface for a single-channel A/D conversion subsystem does not need to
contain more than 2 or 3 bytes of control and status information but it would
need to contain bits for:
- Enabling the interrupt capability
- Indicating errors
- Specifying the sample rate
- Enabling the DMA capability
- Initiating the input (i.e. setting the do bit)
