| AL - 8-bit accumulator AX - 16-bit accumulator CX - Count register DS - Data segment ES - Extra segment Above/below refers to unsigned value Greater = more positive; Less = less positive (more negative) signed values if d = 1 then "to" reg; if d = 0 then "from" reg if w = 1 then word instruction; if w = 0 then byte instruction |
if s w = 01 then 16 bits of immediate data form the operand if s w = 11 then an immediate data byte is sign extended to form the 16-bit operand if v = 0 then "count" = 1 if v = 1 then "count" in (CL) x = don't care z is used for string primitives for comparison with ZF FLAG SEGMENT OVERRIDE PREFIX 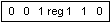 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| if mod = 11 then r/m is treated as a REG field if mod = 00 then DISP = 0* disp-low and disp-high are absent if mod = 01 then DISP = disp-low sign-extended to 16-bits, disp-high is absent if mod = 10 then DISP = 0 disp-high disp-low if r/m = 000 then EA = (BX) + (SI) + DISP if r/m = 001 then EA = (BX) + (DI) + DISP if r/m = 010 then EA = (BP) + (SI) + DISP if r/m = 011 then EA = (BP) + (DI) + DISP if r/m = 100 then EA = (SI) + DISP if r/m = 101 then EA = (DI) + DISP if r/m = 110 then EA = (BP) + DISP if r/m = 111 then EA = (BX) + DISP DISP follows 2nd byte of instruction (before data if required) *except if mod = 00 and r/m = 110 then EA = disp-high disp-low | REG is assigned according to the following table
Instructions which reference the flag register-file as a 16-bit object use the symbol FLAGS to represent the file FLAGS X X X X (OF) (DF) (IF) (TF) (SF) (ZF) X (AF) X (PF) X (CF) |