| Name | Mnemonic and Format | Alternate Mnemonic | Test Condition* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loop | LOOP OPR | (CX) != 0 | ||||
| Loop while zero, or equal | LOOPZ OPR | LOOPE | ZF = 1 and (CX) != 0 | |||
| Loop while nonzero, or not equal | LOOPNZ OPR | LOOPNE | ZF = 0 and (CX) != 0 | |||
| Branch on CX | JCXZ OPR | (CX) = 0 | ||||
*Except for JCXZ which leaves (CX) unchanged, (CX) | ||||||
Flags: No flags are affected. | ||||||
Addressing modes: Mode is relative to IP. OPR must represent a label that is within -128 to 127 bytes of the instruction following the loop instruction. | ||||||
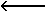 (CX)-1. Then if the test condition is met, (IP)
(CX)-1. Then if the test condition is met, (IP)