| Abbreviation | Meaning | Symbol | Meaning | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPR | Operand | 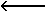 | Replaced by | |||
| SRC | Source operand | 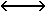 | Interchanged with | |||
| DST | Destination operand | (X) | Contents of X | |||
| REG | Register | 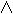 | Logical AND | |||
| RSRC | Source register | 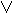 | Logical OR | |||
| RDST | Destination register | 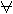 | Logical exclusive OR | |||
| CNT | Count |  X | Complement of X | |||
| DISP | Displacement (general) | |||||
| D8 | 8-bit displacement | |||||
| D16 | 16-bit displacement | |||||
| ADDR | Address | |||||
| EA | Effective address | |||||
| SEG | Segment | |||||
| DATA | Immediate operand (general) | |||||
| DATA8 | 8-bit immediate operand | |||||
| DATA16 | 16-bit immediate operand | |||||
| AX, BX, CX, DX, AL, AH, BL, BH, CL, CH, DL, DH, IP, BP, SP, SI, DI | 8086 register names | |||||
| CS, SS, DS, ES | 8086 segment register names | |||||
| DF, IF, TF | 8086 control flag names | |||||
| OF, SF, ZF, AF, PF, CF | 8086 condition flag names |